.addClass()
Adds the specified class(es) to each element in the set of matched elements.
jQuery is a JavaScript Library.
jQuery greatly simplifies JavaScript programming.
jQuery is easy to learn.
With our online editor, you can edit the code, and click on a button to view the result.
Click on the "Try it Yourself" button to see how it works.
Start learning jQuery now!Learn by examples! At W3Schools you will find a lot of jQuery examples to edit and test yourself.
jQuery ExamplesTest your jQuery skills at W3Schools!
jQuery QuizAt W3Schools you will find a complete reference of all jQuery objects and methods.
jQuery ReferenceThe HTML Certificate documents your knowledge of HTML.
The CSS Certificate documents your knowledge of advanced CSS.
The JavaScript Certificate documents your knowledge of JavaScript and HTML DOM.
The jQuery Certificate documents your knowledge of jQuery.
The PHP Certificate documents your knowledge of PHP and SQL (MySQL).
The XML Certificate documents your knowledge of XML, XML DOM and XSLT.
The Bootstrap Certificate documents your knowledge of the Bootstrap framework.
The purpose of jQuery is to make it much easier to use JavaScript on your website.
Before you start studying jQuery, you should have a basic knowledge of:
If you want to study these subjects first, find the tutorials on our Home page.
jQuery is a lightweight, "write less, do more", JavaScript library.
The purpose of jQuery is to make it much easier to use JavaScript on your website.
jQuery takes a lot of common tasks that require many lines of JavaScript code to accomplish, and wraps them into methods that you can call with a single line of code.
jQuery also simplifies a lot of the complicated things from JavaScript, like AJAX calls and DOM manipulation.
The jQuery library contains the following features:
Tip: In addition, jQuery has plugins for almost any task out there.
There are lots of other JavaScript frameworks out there, but jQuery seems to be the most popular, and also the most extendable.
Many of the biggest companies on the Web use jQuery, such as:
Will jQuery work in all browsers?
The jQuery team knows all about cross-browser issues, and they have
written this knowledge into the jQuery library. jQuery will run exactly the same
in all major browsers.
There are several ways to start using jQuery on your web site. You can:
There are two versions of jQuery available for downloading:
Both versions can be downloaded from jQuery.com.
The jQuery library is a single JavaScript file, and you reference it with the HTML <script> tag (notice that the <script> tag should be inside the <head> section):
<head>
<script src="jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
</head>
Tip: Place the downloaded file in the same directory as the pages where you wish to use it.
Do you wonder why we do not have type="text/javascript" inside the <script> tag?
This is not required in HTML5. JavaScript is the default scripting language in HTML5 and in all modern browsers!
If you don't want to download and host jQuery yourself, you can include it from a CDN (Content Delivery Network).
Both Google and Microsoft host jQuery.
To use jQuery from Google or Microsoft, use one of the following:
<head>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
Try it Yourself »
<head>
<script src="https://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jQuery/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
</head>
Try it Yourself »
One big advantage of using the hosted jQuery from Google or Microsoft:
Many users already have downloaded jQuery from Google or Microsoft when visiting
another site. As a result, it will be loaded from cache when they visit your site, which leads to faster loading time.
Also, most CDN's will make sure that once a user requests a file from it, it will be served
from the server closest to them, which also leads to faster loading time.
With jQuery you select (query) HTML elements and perform "actions" on them.
The jQuery syntax is tailor-made for selecting HTML elements and performing some action on the element(s).
Basic syntax is: $(selector).action()
Examples:
$(this).hide() - hides the current element.
$("p").hide() - hides all <p> elements.
$(".test").hide() - hides all elements with class="test".
$("#test").hide() - hides the element with id="test".
Are you familiar with CSS selectors?
jQuery uses CSS syntax to select elements. You will learn more about the selector syntax in the next chapter of this tutorial.
You might have noticed that all jQuery methods in our examples, are inside a document ready event:
$(document).ready(function(){
// jQuery methods go here...
});
This is to prevent any jQuery code from running before the document is finished loading (is ready).
It is good practice to wait for the document to be fully loaded and ready before working with it. This also allows you to have your JavaScript code before the body of your document, in the head section.
Here are some examples of actions that can fail if methods are run before the document is fully loaded:
Tip: The jQuery team has also created an even shorter method for the document ready event:
$(function(){
// jQuery methods go here...
});
Use the syntax you prefer. We think that the document ready event is easier to understand when reading the code.
jQuery selectors are one of the most important parts of the jQuery library.
jQuery selectors allow you to select and manipulate HTML element(s).
jQuery selectors are used to "find" (or select) HTML elements based on their name, id, classes, types, attributes, values of attributes and much more. It's based on the existing CSS Selectors, and in addition, it has some own custom selectors.
All selectors in jQuery start with the dollar sign and parentheses: $().
The jQuery element selector selects elements based on the element name.
You can select all <p> elements on a page like this:
$("p")
Example
When a user clicks on a button, all <p> elements will be hidden:
The jQuery #id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML tag to find the specific element.
An id should be unique within a page, so you should use the #id selector when you want to find a single, unique element.
To find an element with a specific id, write a hash character, followed by the id of the HTML element:
$("#test")
Example
When a user clicks on a button, the element with id="test" will be hidden:
The jQuery class selector finds elements with a specific class.
To find elements with a specific class, write a period character, followed by the name of the class:
$(".test")
Example
When a user clicks on a button, the elements with class="test" will be hidden:
| Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| $("*") | Selects all elements | Try it |
| $(this) | Selects the current HTML element | Try it |
| $("p.intro") | Selects all <p> elements with class="intro" | Try it |
| $("p:first") | Selects the first <p> element | Try it |
| $("ul li:first") | Selects the first <li> element of the first <ul> | Try it |
| $("ul li:first-child") | Selects the first <li> element of every <ul> | Try it |
| $("[href]") | Selects all elements with an href attribute | Try it |
| $("a[target='_blank']") | Selects all <a> elements with a target attribute value equal to "_blank" | Try it |
| $("a[target!='_blank']") | Selects all <a> elements with a target attribute value NOT equal to "_blank" | Try it |
| $(":button") | Selects all <button> elements and <input> elements of type="button" | Try it |
| $("tr:even") | Selects all even <tr> elements | Try it |
| $("tr:odd") | Selects all odd <tr> elements | Try it |
Use our jQuery Selector Tester to demonstrate the different selectors.
For a complete reference of all the jQuery selectors, please go to our jQuery Selectors Reference.
If your website contains a lot of pages, and you want your jQuery functions to be easy to maintain, you can put your jQuery functions in a separate .js file.
When we demonstrate jQuery in this tutorial, the functions are added directly into the <head> section. However, sometimes it is preferable to place them in a separate file, like this (use the src attribute to refer to the .js file):
<head>
<script
src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script src="my_jquery_functions.js"></script>
</head>
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 » Exercise 5 » Exercise 6 »
jQuery is tailor-made to respond to events in an HTML page.
All the different visitor's actions that a web page can respond to are called events.
An event represents the precise moment when something happens.
Examples:
The term "fires/fired" is often used with events. Example: "The keypress event is fired, the moment you press a key".
Here are some common DOM events:
| Mouse Events | Keyboard Events | Form Events | Document/Window Events |
|---|---|---|---|
| click | keypress | submit | load |
| dblclick | keydown | change | resize |
| mouseenter | keyup | focus | scroll |
| mouseleave | blur | unload |
In jQuery, most DOM events have an equivalent jQuery method.
To assign a click event to all paragraphs on a page, you can do this:
$("p").click();
The next step is to define what should happen when the event fires. You must pass a function to the event:
$("p").click(function(){
// action goes here!!
});
$(document).ready()
The $(document).ready() method allows us to execute a function when the document is fully loaded. This event is already explained in the jQuery Syntax chapter.
click()
The click() method attaches an event handler function to an HTML element.
The function is executed when the user clicks on the HTML element.
The following example says: When a click event fires on a <p> element; hide the current <p> element:
dblclick()
The dblclick() method attaches an event handler function to an HTML element.
The function is executed when the user double-clicks on the HTML element:
mouseenter()
The mouseenter() method attaches an event handler function to an HTML element.
The function is executed when the mouse pointer enters the HTML element:
mouseleave()
The mouseleave() method attaches an event handler function to an HTML element.
The function is executed when the mouse pointer leaves the HTML element:
mousedown()
The mousedown() method attaches an event handler function to an HTML element.
The function is executed, when the left, middle or right mouse button is pressed down, while the mouse is over the HTML element:
mouseup()
The mouseup() method attaches an event handler function to an HTML element.
The function is executed, when the left, middle or right mouse button is released, while the mouse is over the HTML element:
hover()
The hover() method takes two functions and is a combination of the mouseenter() and mouseleave() methods.
The first function is executed when the mouse enters the HTML element, and the second function is executed when the mouse leaves the HTML element:
focus()
The focus() method attaches an event handler function to an HTML form field.
The function is executed when the form field gets focus:
blur()
The blur() method attaches an event handler function to an HTML form field.
The function is executed when the form field loses focus:
The on() method attaches one or more event handlers for the selected elements.
Attach a click event to a <p> element:
Attach multiple event handlers to a <p> element:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 » Exercise 5 »
For a full jQuery event reference, please go to our jQuery Events Reference.
Hide, Show, Toggle, Slide, Fade, and Animate. WOW!
Click to show/hide panel
Because time is valuable, we deliver quick and easy learning.
At W3Schools, you can study everything you need to learn, in an accessible and handy format.
jQuery hide()
Demonstrates a simple jQuery hide() method.
jQuery hide()
Another hide() demonstration. How to hide parts of text.
With jQuery, you can hide and show HTML elements with the hide() and show() methods:
Syntax:
$(selector).hide(speed,callback);
$(selector).show(speed,callback);
The optional speed parameter specifies the speed of the hiding/showing, and can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the hide() or show() method completes (you will learn more about callback functions in a later chapter).
The following example demonstrates the speed parameter with hide():
With jQuery, you can toggle between the hide() and show() methods with the toggle() method.
Shown elements are hidden and hidden elements are shown:
Syntax:
$(selector).toggle(speed,callback);
The optional speed parameter can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after toggle() completes.
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery effects, please go to our jQuery Effect Reference.
With jQuery you can fade elements in and out of visibility.
Click to fade in/out panel
Because time is valuable, we deliver quick and easy learning.
At W3Schools, you can study everything you need to learn, in an accessible and handy format.
jQuery fadeIn()
Demonstrates the jQuery fadeIn() method.
jQuery fadeOut()
Demonstrates the jQuery fadeOut() method.
jQuery
fadeToggle()
Demonstrates the jQuery fadeToggle() method.
jQuery fadeTo()
Demonstrates the jQuery fadeTo() method.
With jQuery you can fade an element in and out of visibility.
jQuery has the following fade methods:
The jQuery fadeIn() method is used to fade in a hidden element.
Syntax:
$(selector).fadeIn(speed,callback);
The optional speed parameter specifies the duration of the effect. It can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the fading completes.
The following example demonstrates the fadeIn() method with different parameters:
The jQuery fadeOut() method is used to fade out a visible element.
Syntax:
$(selector).fadeOut(speed,callback);
The optional speed parameter specifies the duration of the effect. It can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the fading completes.
The following example demonstrates the fadeOut() method with different parameters:
The jQuery fadeToggle() method toggles between the fadeIn() and fadeOut() methods.
If the elements are faded out, fadeToggle() will fade them in.
If the elements are faded in, fadeToggle() will fade them out.
Syntax:
$(selector).fadeToggle(speed,callback);
The optional speed parameter specifies the duration of the effect. It can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the fading completes.
The following example demonstrates the fadeToggle() method with different parameters:
The jQuery fadeTo() method allows fading to a given opacity (value between 0 and 1).
Syntax:
$(selector).fadeTo(speed,opacity,callback);
The required speed parameter specifies the duration of the effect. It can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The required opacity parameter in the fadeTo() method specifies fading to a given opacity (value between 0 and 1).
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the function completes.
The following example demonstrates the fadeTo() method with different parameters:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 » Exercise 5 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery effects, please go to our jQuery Effect Reference.
The jQuery slide methods slide elements up and down.
Click to slide down/up the panel
Because time is valuable, we deliver quick and easy learning.
At W3Schools, you can study everything you need to learn, in an accessible and handy format.
jQuery slideDown()
Demonstrates the jQuery slideDown() method.
jQuery slideUp()
Demonstrates the jQuery slideUp() method.
jQuery slideToggle()
Demonstrates the jQuery slideToggle() method.
With jQuery you can create a sliding effect on elements.
jQuery has the following slide methods:
The jQuery slideDown() method is used to slide down an element.
Syntax:
$(selector).slideDown(speed,callback);
The optional speed parameter specifies the duration of the effect. It can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the sliding completes.
The following example demonstrates the slideDown() method:
The jQuery slideUp() method is used to slide up an element.
Syntax:
$(selector).slideUp(speed,callback);
The optional speed parameter specifies the duration of the effect. It can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the sliding completes.
The following example demonstrates the slideUp() method:
The jQuery slideToggle() method toggles between the slideDown() and slideUp() methods.
If the elements have been slid down, slideToggle() will slide them up.
If the elements have been slid up, slideToggle() will slide them down.
$(selector).slideToggle(speed,callback);
The optional speed parameter can take the following values: "slow", "fast", milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the sliding completes.
The following example demonstrates the slideToggle() method:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery effects, please go to our jQuery Effect Reference.
The jQuery animate() method lets you create custom animations.
The jQuery animate() method is used to create custom animations.
Syntax:
$(selector).animate({params},speed,callback);
The required params parameter defines the CSS properties to be animated.
The optional speed parameter specifies the duration of the effect. It can take the following values: "slow", "fast", or milliseconds.
The optional callback parameter is a function to be executed after the animation completes.
The following example demonstrates a simple use of the animate() method; it moves a <div> element to the right, until it has reached a left property of 250px:
By default, all HTML elements have a static position, and cannot be moved.
To manipulate the position, remember to first set the CSS position property of the element to relative, fixed, or absolute!
Notice that multiple properties can be animated at the same time:
Is it possible to manipulate ALL CSS properties with the animate() method?
Yes, almost! However, there is one important thing to remember: all property
names must be camel-cased when used with the animate() method: You will need to
write paddingLeft instead of padding-left, marginRight instead of margin-right, and so on.
Also, color animation is not included in the core jQuery library.
If you want to animate color, you need to download the
Color
Animations plugin from jQuery.com.
It is also possible to define relative values (the value is then relative to the element's current value). This is done by putting += or -= in front of the value:
You can even specify a property's animation value as "show", "hide", or "toggle":
By default, jQuery comes with queue functionality for animations.
This means that if you write multiple animate() calls after each other, jQuery creates an "internal" queue with these method calls. Then it runs the animate calls ONE by ONE.
So, if you want to perform different animations after each other, we take advantage of the queue functionality:
The example below first moves the <div> element to the right, and then increases the font size of the text:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery effects, please go to our jQuery Effect Reference.
The jQuery stop() method is used to stop animations or effects before it is finished.
Click to slide down/up the panel
Because time is valuable, we deliver quick and easy learning.
At W3Schools, you can study everything you need to learn, in an accessible and handy format.
jQuery stop() sliding
Demonstrates the jQuery stop() method.
jQuery
stop() animation (with parameters)
Demonstrates the jQuery stop() method.
The jQuery stop() method is used to stop an animation or effect before it is finished.
The stop() method works for all jQuery effect functions, including sliding, fading and custom animations.
Syntax:
$(selector).stop(stopAll,goToEnd);
The optional stopAll parameter specifies whether also the animation queue should be cleared or not. Default is false, which means that only the active animation will be stopped, allowing any queued animations to be performed afterwards.
The optional goToEnd parameter specifies whether or not to complete the current animation immediately. Default is false.
So, by default, the stop() method kills the current animation being performed on the selected element.
The following example demonstrates the stop() method, with no parameters:
For a complete overview of all jQuery effects, please go to our jQuery Effect Reference.
A callback function is executed after the current effect is 100% finished.
JavaScript statements are executed line by line. However, with effects, the next line of code can be run even though the effect is not finished. This can create errors.
To prevent this, you can create a callback function.
A callback function is executed after the current effect is finished.
Typical syntax: $(selector).hide(speed,callback);
Examples
The example below has a callback parameter that is a function that will be executed after the hide effect is completed:
The example below has no callback parameter, and the alert box will be displayed before the hide effect is completed:
With jQuery, you can chain together actions/methods.
Chaining allows us to run multiple jQuery methods (on the same element) within a single statement.
Until now we have been writing jQuery statements one at a time (one after the other).
However, there is a technique called chaining, that allows us to run multiple jQuery commands, one after the other, on the same element(s).
Tip: This way, browsers do not have to find the same element(s) more than once.
To chain an action, you simply append the action to the previous action.
The following example chains together the css(), slideUp(), and slideDown() methods. The "p1" element first changes to red, then it slides up, and then it slides down:
We could also have added more method calls if needed.
Tip: When chaining, the line of code could become quite long. However, jQuery is not very strict on the syntax; you can format it like you want, including line breaks and indentations.
This also works just fine:
jQuery throws away extra whitespace and executes the lines above as one long line of code.
jQuery contains powerful methods for changing and manipulating HTML elements and attributes.
One very important part of jQuery is the possibility to manipulate the DOM.
jQuery comes with a bunch of DOM related methods that make it easy to access and manipulate elements and attributes.
DOM = Document Object Model
The DOM defines a standard for accessing HTML and XML documents:
"The W3C Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform and language-neutral
interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the
content, structure, and style of a document."
Three simple, but useful, jQuery methods for DOM manipulation are:
The following example demonstrates how to get content with the jQuery text() and html() methods:
The following example demonstrates how to get the value of an input field with the jQuery val() method:
The jQuery attr() method is used to get attribute values.
The following example demonstrates how to get the value of the href attribute in a link:
The next chapter explains how to set (change) content and attribute values.
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery HTML methods, please go to our jQuery HTML/CSS Reference.
We will use the same three methods from the previous page to set content:
The following example demonstrates how to set content with the jQuery text(), html(), and val() methods:
All of the three jQuery methods above: text(), html(), and val(), also come with a callback function. The callback function has two parameters: the index of the current element in the list of elements selected and the original (old) value. You then return the string you wish to use as the new value from the function.
The following example demonstrates text() and html() with a callback function:
The jQuery attr() method is also used to set/change attribute values.
The following example demonstrates how to change (set) the value of the href attribute in a link:
The attr() method also allows you to set multiple attributes at the same time.
The following example demonstrates how to set both the href and title attributes at the same time:
The jQuery method attr(), also come with a callback function. The callback function has two parameters: the index of the current element in the list of elements selected and the original (old) attribute value. You then return the string you wish to use as the new attribute value from the function.
The following example demonstrates attr() with a callback function:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 » Exercise 5 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery HTML methods, please go to our jQuery HTML/CSS Reference.
With jQuery, it is easy to add new elements/content.
We will look at four jQuery methods that are used to add new content:
The jQuery append() method inserts content AT THE END of the selected HTML elements.
The jQuery prepend() method inserts content AT THE BEGINNING of the selected HTML elements.
In both examples above, we have only inserted some text/HTML at the beginning/end of the selected HTML elements.
However, both the append() and prepend() methods can take an infinite number of new elements as parameters. The new elements can be generated with text/HTML (like we have done in the examples above), with jQuery, or with JavaScript code and DOM elements.
In the following example, we create several new elements. The elements are created with text/HTML, jQuery, and JavaScript/DOM. Then we append the new elements to the text with the append() method (this would have worked for prepend() too) :
The jQuery after() method inserts content AFTER the selected HTML elements.
The jQuery before() method inserts content BEFORE the selected HTML elements.
Also, both the after() and before() methods can take an infinite number of new elements as parameters. The new elements can be generated with text/HTML (like we have done in the example above), with jQuery, or with JavaScript code and DOM elements.
In the following example, we create several new elements. The elements are created with text/HTML, jQuery, and JavaScript/DOM. Then we insert the new elements to the text with the after() method (this would have worked for before() too) :
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery HTML methods, please go to our jQuery HTML/CSS Reference.
With jQuery, it is easy to remove existing HTML elements.
To remove elements and content, there are mainly two jQuery methods:
The jQuery remove() method removes the selected element(s) and its child elements.
The jQuery empty() method removes the child elements of the selected element(s).
The jQuery remove() method also accepts one parameter, which allows you to filter the elements to be removed.
The parameter can be any of the jQuery selector syntaxes.
The following example removes all <p> elements with class="test":
This example removes all <p> elements with class="test" and class="demo":
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery HTML methods, please go to our jQuery HTML/CSS Reference.
With jQuery, it is easy to manipulate the CSS of elements.
jQuery has several methods for CSS manipulation. We will look at the following methods:
The following stylesheet will be used for all the examples on this page:
.important
{
font-weight: bold;
font-size: xx-large;
}
.blue
{
color: blue;
}
The following example shows how to add class attributes to different elements. Of course you can select multiple elements, when adding classes:
You can also specify multiple classes within the addClass() method:
The following example shows how to remove a specific class attribute from different elements:
The following example will show how to use the jQuery toggleClass() method. This method toggles between adding/removing classes from the selected elements:
The jQuery css() method will be explained in the next chapter.
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery CSS methods, please go to our jQuery HTML/CSS Reference.
The css() method sets or returns one or more style properties for the selected elements.
To return the value of a specified CSS property, use the following syntax:
css("propertyname");
The following example will return the background-color value of the FIRST matched element:
To set a specified CSS property, use the following syntax:
css("propertyname","value");
The following example will set the background-color value for ALL matched elements:
To set multiple CSS properties, use the following syntax:
css({"propertyname":"value","propertyname":"value",...});
The following example will set a background-color and a font-size for ALL matched elements:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery CSS methods, please go to our jQuery HTML/CSS Reference.
With jQuery, it is easy to work with the dimensions of elements and browser window.
jQuery has several important methods for working with dimensions:
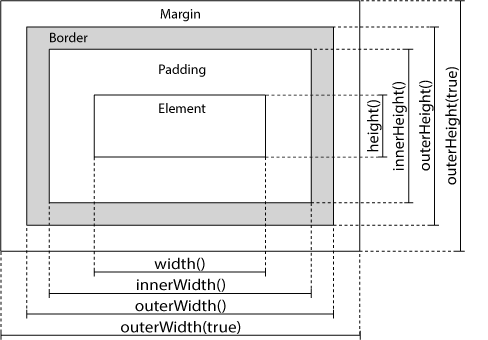
The width() method sets or returns the width of an element (excludes padding, border and margin).
The height() method sets or returns the height of an element (excludes padding, border and margin).
The following example returns the width and height of a specified <div> element:
The innerWidth() method returns the width of an element (includes padding).
The innerHeight() method returns the height of an element (includes padding).
The following example returns the inner-width/height of a specified <div> element:
The outerWidth() method returns the width of an element (includes padding and border).
The outerHeight() method returns the height of an element (includes padding and border).
The following example returns the outer-width/height of a specified <div> element:
The outerWidth(true) method returns the width of an element (includes padding, border, and margin).
The outerHeight(true) method returns the height of an element (includes padding, border, and margin).
The following example returns the width and height of the document (the HTML document) and window (the browser viewport):
The following example sets the width and height of a specified <div> element:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 » Exercise 5 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery CSS methods, please go to our jQuery HTML/CSS Reference.
jQuery traversing, which means "move through", are used to "find" (or select) HTML elements based on their relation to other elements. Start with one selection and move through that selection until you reach the elements you desire.
The image below illustrates an HTML page as a tree (DOM tree). With jQuery traversing, you can easily move up (ancestors), down (descendants) and sideways (siblings) in the tree, starting from the selected (current) element. This movement is called traversing - or moving through - the DOM tree.
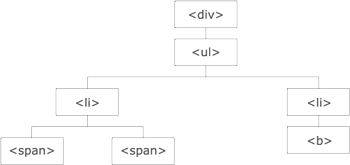
Illustration explained:
An ancestor is a parent, grandparent, great-grandparent, and so on.
A
descendant is a child, grandchild, great-grandchild, and so on.
Siblings share the same parent.
jQuery provides a variety of methods that allow us to traverse the DOM.
The largest category of traversal methods are tree-traversal.
The next chapters will show us how to travel up, down and sideways in the DOM tree.
For a complete overview of all jQuery Traversing methods, please go to our jQuery Traversing Reference.
An ancestor is a parent, grandparent, great-grandparent, and so on.
With jQuery you can traverse up the DOM tree to find ancestors of an element.
Three useful jQuery methods for traversing up the DOM tree are:
The parent() method returns the direct parent element of the selected element.
This method only traverse a single level up the DOM tree.
The following example returns the direct parent element of each <span> elements:
The parents() method returns all ancestor elements of the selected element, all the way up to the document's root element (<html>).
The following example returns all ancestors of all <span> elements:
You can also use an optional parameter to filter the search for ancestors.
The following example returns all ancestors of all <span> elements that are <ul> elements:
The parentsUntil() method returns all ancestor elements between two given arguments.
The following example returns all ancestor elements between a <span> and a <div> element:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery Traversing methods, please go to our jQuery Traversing Reference.
A descendant is a child, grandchild, great-grandchild, and so on.
With jQuery you can traverse down the DOM tree to find descendants of an element.
Two useful jQuery methods for traversing down the DOM tree are:
The children() method returns all direct children of the selected element.
This method only traverse a single level down the DOM tree.
The following example returns all elements that are direct children of each <div> elements:
You can also use an optional parameter to filter the search for children.
The following example returns all <p> elements with the class name "first", that are direct children of <div>:
The find() method returns descendant elements of the selected element, all the way down to the last descendant.
The following example returns all <span> elements that are descendants of <div>:
The following example returns all descendants of <div>:
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery Traversing methods, please go to our jQuery Traversing Reference.
With jQuery you can traverse sideways in the DOM tree to find siblings of an element.
Siblings share the same parent.
There are many useful jQuery methods for traversing sideways in the DOM tree:
The siblings() method returns all sibling elements of the selected element.
The following example returns all sibling elements of <h2>:
You can also use an optional parameter to filter the search for siblings.
The following example returns all sibling elements of <h2> that are <p> elements:
The next() method returns the next sibling element of the selected element.
The following example returns the next sibling of <h2>:
The nextAll() method returns all next sibling elements of the selected element.
The following example returns all next sibling elements of <h2>:
The nextUntil() method returns all next sibling elements between two given arguments.
The following example returns all sibling elements between a <h2> and a <h6> element:
The prev(), prevAll() and prevUntil() methods work just like the methods above but with reverse functionality: they return previous sibling elements (traverse backwards along sibling elements in the DOM tree, instead of forward).
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 » Exercise 5 » Exercise 6 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery Traversing methods, please go to our jQuery Traversing Reference.
The most basic filtering methods are first(), last() and eq(), which allow you to select a specific element based on its position in a group of elements.
Other filtering methods, like filter() and not() allow you to select elements that match, or do not match, a certain criteria.
The first() method returns the first element of the specified elements.
The following example selects the first <div> element:
The last() method returns the last element of the specified elements.
The following example selects the last <div> element:
The eq() method returns an element with a specific index number of the selected elements.
The index numbers start at 0, so the first element will have the index number 0 and not 1. The following example selects the second <p> element (index number 1):
The filter() method lets you specify a criteria. Elements that do not match the criteria are removed from the selection, and those that match will be returned.
The following example returns all <p> elements with class name "intro":
The not() method returns all elements that do not match the criteria.
Tip: The not() method is the opposite of filter().
The following example returns all <p> elements that do not have class name "intro":
Exercise 1 » Exercise 2 » Exercise 3 » Exercise 4 » Exercise 5 » Exercise 6 »
For a complete overview of all jQuery Traversing methods, please go to our jQuery Traversing Reference.
AJAX is the art of exchanging data with a server, and updating parts of a web page - without reloading the whole page.
AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript and XML.
In short; AJAX is about loading data in the background and display it on the webpage, without reloading the whole page.
Examples of applications using AJAX: Gmail, Google Maps, Youtube, and Facebook tabs.
You can learn more about AJAX in our AJAX tutorial.
jQuery provides several methods for AJAX functionality.
With the jQuery AJAX methods, you can request text, HTML, XML, or JSON from a remote server using both HTTP Get and HTTP Post - And you can load the external data directly into the selected HTML elements of your web page!
Without jQuery, AJAX coding can be a bit tricky!
Writing regular AJAX code can be a bit tricky, because different browsers have different
syntax for AJAX implementation. This means that you will have to write extra code
to test for different browsers. However, the jQuery team has taken care of this
for us, so that we can write AJAX functionality with only one single line of code.
In the next chapters we will look at the most important jQuery AJAX methods.
The jQuery load() method is a simple, but powerful AJAX method.
The load() method loads data from a server and puts the returned data into the selected element.
Syntax:
$(selector).load(URL,data,callback);
The required URL parameter specifies the URL you wish to load.
The optional data parameter specifies a set of querystring key/value pairs to send along with the request.
The optional callback parameter is the name of a function to be executed after the load() method is completed.
Here is the content of our example file: "demo_test.txt":
<h2>jQuery and AJAX is FUN!!!</h2>
<p id="p1">This is some text in a paragraph.</p>
The following example loads the content of the file "demo_test.txt" into a specific <div> element:
It is also possible to add a jQuery selector to the URL parameter.
The following example loads the content of the element with id="p1", inside the file "demo_test.txt", into a specific <div> element:
The optional callback parameter specifies a callback function to run when the load() method is completed. The callback function can have different parameters:
The following example displays an alert box after the load() method completes. If the load() method has succeeded, it displays "External content loaded successfully!", and if it fails it displays an error message:
For a complete overview of all jQuery AJAX methods, please go to our jQuery AJAX Reference.
The jQuery get() and post() methods are used to request data from the server with an HTTP GET or POST request.
Two commonly used methods for a request-response between a client and server are: GET and POST.
GET is basically used for just getting (retrieving) some data from the server. Note: The GET method may return cached data.
POST can also be used to get some data from the server. However, the POST method NEVER caches data, and is often used to send data along with the request.
To learn more about GET and POST, and the differences between the two methods, please read our HTTP Methods GET vs POST chapter.
The $.get() method requests data from the server with an HTTP GET request.
Syntax:
$.get(URL,callback);
The required URL parameter specifies the URL you wish to request.
The optional callback parameter is the name of a function to be executed if the request succeeds.
The following example uses the $.get() method to retrieve data from a file on the server:
The first parameter of $.get() is the URL we wish to request ("demo_test.asp").
The second parameter is a callback function. The first callback parameter holds the content of the page requested, and the second callback parameter holds the status of the request.
Tip: Here is how the ASP file looks like ("demo_test.asp"):
<%
response.write("This is some text from an external ASP file.")
%>
The $.post() method requests data from the server using an HTTP POST request.
Syntax:
$.post(URL,data,callback);
The required URL parameter specifies the URL you wish to request.
The optional data parameter specifies some data to send along with the request.
The optional callback parameter is the name of a function to be executed if the request succeeds.
The following example uses the $.post() method to send some data along with the request:
The first parameter of $.post() is the URL we wish to request ("demo_test_post.asp").
Then we pass in some data to send along with the request (name and city).
The ASP script in "demo_test_post.asp" reads the parameters, processes them, and returns a result.
The third parameter is a callback function. The first callback parameter holds the content of the page requested, and the second callback parameter holds the status of the request.
Tip: Here is how the ASP file looks like ("demo_test_post.asp"):
<%
dim fname,city
fname=Request.Form("name")
city=Request.Form("city")
Response.Write("Dear " & fname & ". ")
Response.Write("Hope you live well in " & city & ".")
%>
For a complete overview of all jQuery AJAX methods, please go to our jQuery AJAX Reference.
What if you wish to use other frameworks on your pages, while still using jQuery?
As you already know; jQuery uses the $ sign as a shortcut for jQuery.
There are many other popular JavaScript frameworks like: Angular, Backbone, Ember, Knockout, and more.
What if other JavaScript frameworks also use the $ sign as a shortcut?
If two different frameworks are using the same shortcut, one of them might stop working.
The jQuery team have already thought about this, and implemented the noConflict() method.
The noConflict() method releases the hold on the $ shortcut identifier, so that other scripts can use it.
You can of course still use jQuery, simply by writing the full name instead of the shortcut:
You can also create your own shortcut very easily. The noConflict() method returns a reference to jQuery, that you can save in a variable, for later use. Here is an example:
If you have a block of jQuery code which uses the $ shortcut and you do not want to change it all, you can pass the $ sign in as a parameter to the ready method. This allows you to access jQuery using $, inside this function - outside of it, you will have to use "jQuery":
For a complete overview of all jQuery Misc methods, please go to our jQuery Misc Reference.
Use jQuery to filter/search for specific elements.
Perform a case-insensitive search for items in a table:
Type something in the input field to search the table for first names, last names or emails:
| Firstname | Lastname | |
|---|---|---|
| John | Doe | john@example.com |
| Mary | Moe | mary@mail.com |
| July | Dooley | july@greatstuff.com |
| Anja | Ravendale | a_r@test.com |
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#myInput").on("keyup", function() {
var value = $(this).val().toLowerCase();
$("#myTable tr").filter(function() {
$(this).toggle( $(this).text().toLowerCase().indexOf(value) > -1 );
});
});
});
</script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#myInput").on("keyup", function() {
var
value = $(this).val().toLowerCase();
$("#myTable tr").filter(function() {
$(this).toggle($(this).text().toLowerCase().indexOf(value) > -1)
});
});
});
</script>
Try it Yourself »
Example explained: We use jQuery to loop through each table
rows to check if there are any text values that matches the value of the input
field. The toggle method hides the row (display:none) that does not match the
search. We use the toLowerCase() DOM method to convert the text to lower case, which
makes the search case insensitive (allows "john", "John", and even "JOHN" on
search).
Perform a case-insensitive search for items in a list:
Type something in the input field to search the list for items:
Perform a case-insensitive search for text inside a div element:
I am a paragraph.
Another paragraph.
Do you want to develop your jQuery selector skills?
Please try our jQuery Selector Tester
$("p").hide()
Demonstrates the jQuery hide() method, hiding all <p> elements.
$("#test").hide()
Demonstrates the jQuery hide() method, hiding the element with id="test".
$(".test").hide()
Demonstrates the jQuery hide() method, hiding all elements with class="test".
$(this).hide()
Demonstrates the jQuery hide() method, hiding the current HTML element.
jQuery click()
Demonstrates the jQuery click() event.
jQuery
dblclick()
Demonstrates the jQuery dblclick() event.
jQuery
mouseenter()
Demonstrates the jQuery mouseenter() event.
jQuery
mouseleave()
Demonstrates the jQuery mouseleave() event.
jQuery
mousedown()
Demonstrates the jQuery mousedown() event.
jQuery mouseup()
Demonstrates the jQuery mouseup() event.
jQuery hover()
Demonstrates the jQuery hover() event.
jQuery
focus() and blur()
Demonstrates the jQuery focus() and blur() events.
jQuery hide()
Demonstrates the jQuery hide() method.
jQuery
hide() and show()
Demonstrates jQuery hide() and show() methods.
jQuery toggle()
jQuery toggle() toggles between hide() and show().
jQuery hide()
Another hide demonstration. How to hide parts of text.
jQuery fadeIn()
Demonstrates the jQuery fadeIn() method.
jQuery fadeOut()
Demonstrates the jQuery fadeOut() method.
jQuery fadeToggle()
Demonstrates the jQuery fadeToggle() method.
jQuery fadeTo()
Demonstrates the jQuery fadeTo() method.
jQuery slideDown()
Demonstrates the jQuery slideDown() method.
jQuery slideUp()
Demonstrates the jQuery slideUp() method.
jQuery slideToggle()
Demonstrates the jQuery slideToggle() method.
jQuery animate()
Demonstrates a simple use of the jQuery animate() method.
jQuery animate() - manipulate multiple CSS properties
Demonstrates that you can manipulate multiple CSS properties with the jQuery animate() method.
jQuery animate() - using relative values
Demonstrates that you can use relative values in the jQuery animate() method.
jQuery animate() - using pre-defined values
Demonstrates that you can use the pre-defined values "hide", "show", "toggle" in the jQuery animate() method.
jQuery animate()
Demonstrates more using the jQuery animate() method (several animate() calls after each other).
jQuery animate()
Demonstrates more using the jQuery animate() method (several animate() calls after each other).
jQuery stop() sliding
Demonstrates the jQuery stop() method.
jQuery stop() animation (with parameters)
Demonstrates the jQuery stop() method.
jQuery text() and html() - Get content
Get content with the jQuery text() and html() methods.
jQuery val() - Get content
Get the value of a form field with the jQuery val() method.
jQuery attr() - Get attribute value
Get the value of an attribute with the jQuery attr() method.
jQuery text(), html(), and val() - Set content
Set content with the jQuery text(), html() and val() methods.
jQuery text() and html() - Set content with a callback function
Set content + using a callback function inside text() and html().
jQuery attr() - Set attribute value
Set attribute value with the jQuery attr() method.
jQuery attr() - Set multiple attribute values
Set multiple attribute values with the jQuery attr() method.
jQuery attr() - Set attribute value with a callback function
Set attribute value + using a callback function inside attr().
jQuery append()
Insert content at the end of the selected HTML elements.
jQuery prepend()
Insert content at the beginning of the selected HTML elements.
jQuery append() - Insert several new elements
Create new elements with text/HTML, jQuery, and JavaScript/DOM. Then append the new elements to the text.
jQuery after() and before()
Insert content after and before the selected HTML elements.
jQuery after() - Insert several new elements
Create new elements with text/HTML, jQuery, and JavaScript/DOM. Then insert the new elements after the selected element.
jQuery remove()
Remove the selected element(s).
jQuery empty()
Remove all child elements of the selected element(s).
jQuery remove() - with a parameter
Filter the elements to be removed
jQuery addClass()
Add class attributes to different elements.
jQuery addClass() - Multiple classes
Specify multiple classes within the addClass() method.
jQuery removeClass()
Remove a specific class attribute from different elements.
jQuery toggleClass()
Toggle between adding/removing classes from the selected elements.
jQuery css() - return CSS property
Return the value of a specified CSS property from the FIRST matched element.
jQuery css() - set CSS property
Set a specified CSS property for ALL matched elements.
jQuery css() - set CSS properties
Set multiple CSS properties for ALL matched elements.
jQuery - return width() and height()
Return the width and height of a specified element.
jQuery - return innerWidth() and innerHeight()
Return the inner-width/height of a specified element.
jQuery - return outerWidth() and outerHeight()
Return the outer-width/height of a specified element.
jQuery - return outerWidth(true) and outerHeight(true)
Return the outer-width/height (including margins) of a specified element.
jQuery - return width() and height() of document and window
Return the width and height of the document (the HTML document) and window (the
browser viewport).
jQuery - set width() and height()
Sets the width and height of a specified element.
jQuery parent()
Demonstrates the jQuery parent() method.
jQuery parents()
Demonstrates the jQuery parents() method.
jQuery parentsUntil()
Demonstrates the jQuery parentsUntil() method.
jQuery children()
Demonstrates the jQuery children() method.
jQuery find()
Demonstrates the jQuery find() method.
jQuery siblings()
Demonstrates the jQuery siblings() method.
jQuery next()
Demonstrates the jQuery next() method.
jQuery nextAll()
Demonstrates the jQuery nextAll() method.
jQuery nextUntil()
Demonstrates the jQuery nextUntil() method.
jQuery first()
Demonstrates the jQuery first() method.
jQuery last()
Demonstrates the jQuery last() method.
jQuery eq()
Demonstrates the jQuery eq() method.
jQuery filter()
Demonstrates the jQuery filter() method.
jQuery not()
Demonstrates the jQuery not() method.
Filter table
Filter/search for elements in a table.
Filter list
Filter/search for elements in a list.
Filter anything
Filter/search for elements in a div element.
jQuery load()
Load the content of a file into a <div> element.
jQuery load()
Load the content of a specific element inside a file, into a <div> element.
jQuery load() - with callback
Use of the jQuery load() method with a callback function.
jQuery get()
Use the $.get() method to retrieve data from a file on the server.
jQuery
post()
Use the $.post() method to send some data along with the request.
You can test your jQuery skills with W3Schools' Quiz.
The test contains 25 questions and there is no time limit.
The test is not official, it's just a nice way to see how much you know, or don't know, about the jQuery library.
You will get 1 point for each correct answer. At the end of the Quiz, your total score will be displayed. Maximum score is 25 points.
Good luck!
The perfect solution for professionals who need to balance work, family, and career building.
More than 10 000 certificates already issued!
The HTML Certificate documents your knowledge of HTML.
The CSS Certificate documents your knowledge of advanced CSS.
The JavaScript Certificate documents your knowledge of JavaScript and HTML DOM.
The jQuery Certificate documents your knowledge of jQuery.
The PHP Certificate documents your knowledge of PHP and SQL (MySQL).
The XML Certificate documents your knowledge of XML, XML DOM and XSLT.
The Bootstrap Certificate documents your knowledge of the Bootstrap framework.
 |
W3Schools offers an Online Certification Program. The perfect solution for busy professionals who need to balance work, family, and career building. More than 15 000 certificates already issued! |
Document Your SkillsKnowledge is power, especially in the current job market. Documentation of your skills enables you to advance your career, or help you to start a new one. Get a CertificateGetting a certificate proves your commitment to upgrade your skills, gives you the credibility needed for more responsibilities, larger projects, and a higher salary. |
Use our jQuery Selector Tester to demonstrate the different selectors.
| Selector | Example | Selects |
|---|---|---|
| * | $("*") | All elements |
| #id | $("#lastname") | The element with id="lastname" |
| .class | $(".intro") | All elements with class="intro" |
| .class,.class | $(".intro,.demo") | All elements with the class "intro" or "demo" |
| element | $("p") | All <p> elements |
| el1,el2,el3 | $("h1,div,p") | All <h1>, <div> and <p> elements |
| :first | $("p:first") | The first <p> element |
| :last | $("p:last") | The last <p> element |
| :even | $("tr:even") | All even <tr> elements |
| :odd | $("tr:odd") | All odd <tr> elements |
| :first-child | $("p:first-child") | All <p> elements that are the first child of their parent |
| :first-of-type | $("p:first-of-type") | All <p> elements that are the first <p> element of their parent |
| :last-child | $("p:last-child") | All <p> elements that are the last child of their parent |
| :last-of-type | $("p:last-of-type") | All <p> elements that are the last <p> element of their parent |
| :nth-child(n) | $("p:nth-child(2)") | All <p> elements that are the 2nd child of their parent |
| :nth-last-child(n) | $("p:nth-last-child(2)") | All <p> elements that are the 2nd child of their parent, counting from the last child |
| :nth-of-type(n) | $("p:nth-of-type(2)") | All <p> elements that are the 2nd <p> element of their parent |
| :nth-last-of-type(n) | $("p:nth-last-of-type(2)") | All <p> elements that are the 2nd <p> element of their parent, counting from the last child |
| :only-child | $("p:only-child") | All <p> elements that are the only child of their parent |
| :only-of-type | $("p:only-of-type") | All <p> elements that are the only child, of its type, of their parent |
| parent > child | $("div > p") | All <p> elements that are a direct child of a <div> element |
| parent descendant | $("div p") | All <p> elements that are descendants of a <div> element |
| element + next | $("div + p") | The <p> element that are next to each <div> elements |
| element ~ siblings | $("div ~ p") | All <p> elements that are siblings of a <div> element |
| :eq(index) | $("ul li:eq(3)") | The fourth element in a list (index starts at 0) |
| :gt(no) | $("ul li:gt(3)") | List elements with an index greater than 3 |
| :lt(no) | $("ul li:lt(3)") | List elements with an index less than 3 |
| :not(selector) | $("input:not(:empty)") | All input elements that are not empty |
| :header | $(":header") | All header elements <h1>, <h2> ... |
| :animated | $(":animated") | All animated elements |
| :focus | $(":focus") | The element that currently has focus |
| :contains(text) | $(":contains('Hello')") | All elements which contains the text "Hello" |
| :has(selector) | $("div:has(p)") | All <div> elements that have a <p> element |
| :empty | $(":empty") | All elements that are empty |
| :parent | $(":parent") | All elements that are a parent of another element |
| :hidden | $("p:hidden") | All hidden <p> elements |
| :visible | $("table:visible") | All visible tables |
| :root | $(":root") | The document's root element |
| :lang(language) | $("p:lang(de)") | All <p> elements with a lang attribute value starting with "de" |
| [attribute] | $("[href]") | All elements with a href attribute |
| [attribute=value] | $("[href='default.htm']") | All elements with a href attribute value equal to "default.htm" |
| [attribute!=value] | $("[href!='default.htm']") | All elements with a href attribute value not equal to "default.htm" |
| [attribute$=value] | $("[href$='.jpg']") | All elements with a href attribute value ending with ".jpg" |
| [attribute|=value] | $("[title|='Tomorrow']") | All elements with a title attribute value equal to 'Tomorrow', or starting with 'Tomorrow' followed by a hyphen |
| [attribute^=value] | $("[title^='Tom']") | All elements with a title attribute value starting with "Tom" |
| [attribute~=value] | $("[title~='hello']") | All elements with a title attribute value containing the specific word "hello" |
| [attribute*=value] | $("[title*='hello']") | All elements with a title attribute value containing the word "hello" |
| :input | $(":input") | All input elements |
| :text | $(":text") | All input elements with type="text" |
| :password | $(":password") | All input elements with type="password" |
| :radio | $(":radio") | All input elements with type="radio" |
| :checkbox | $(":checkbox") | All input elements with type="checkbox" |
| :submit | $(":submit") | All input elements with type="submit" |
| :reset | $(":reset") | All input elements with type="reset" |
| :button | $(":button") | All input elements with type="button" |
| :image | $(":image") | All input elements with type="image" |
| :file | $(":file") | All input elements with type="file" |
| :enabled | $(":enabled") | All enabled input elements |
| :disabled | $(":disabled") | All disabled input elements |
| :selected | $(":selected") | All selected input elements |
| :checked | $(":checked") | All checked input elements |
Event methods trigger or attach a function to an event handler for the selected elements.
The following table lists all the jQuery methods used to handle events.
| Method / Property | Description |
|---|---|
| bind() | Deprecated in version 3.0. Use the on() method instead. Attaches event handlers to elements |
| blur() | Attaches/Triggers the blur event |
| change() | Attaches/Triggers the change event |
| click() | Attaches/Triggers the click event |
| dblclick() | Attaches/Triggers the double click event |
| delegate() | Deprecated in version 3.0. Use the on() method instead. Attaches a handler to current, or future, specified child elements of the matching elements |
| die() | Removed in version 1.9. Removes all event handlers added with the live() method |
| error() | Removed in version 3.0. Attaches/Triggers the error event |
| event.currentTarget | The current DOM element within the event bubbling phase |
| event.data | Contains the optional data passed to an event method when the current executing handler is bound |
| event.delegateTarget | Returns the element where the currently-called jQuery event handler was attached |
| event.isDefaultPrevented() | Returns whether event.preventDefault() was called for the event object |
| event.isImmediatePropagationStopped() | Returns whether event.stopImmediatePropagation() was called for the event object |
| event.isPropagationStopped() | Returns whether event.stopPropagation() was called for the event object |
| event.namespace | Returns the namespace specified when the event was triggered |
| event.pageX | Returns the mouse position relative to the left edge of the document |
| event.pageY | Returns the mouse position relative to the top edge of the document |
| event.preventDefault() | Prevents the default action of the event |
| event.relatedTarget | Returns which element being entered or exited on mouse movement. |
| event.result | Contains the last/previous value returned by an event handler triggered by the specified event |
| event.stopImmediatePropagation() | Prevents other event handlers from being called |
| event.stopPropagation() | Prevents the event from bubbling up the DOM tree, preventing any parent handlers from being notified of the event |
| event.target | Returns which DOM element triggered the event |
| event.timeStamp | Returns the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, when the event is triggered |
| event.type | Returns which event type was triggered |
| event.which | Returns which keyboard key or mouse button was pressed for the event |
| focus() | Attaches/Triggers the focus event |
| focusin() | Attaches an event handler to the focusin event |
| focusout() | Attaches an event handler to the focusout event |
| hover() | Attaches two event handlers to the hover event |
| keydown() | Attaches/Triggers the keydown event |
| keypress() | Attaches/Triggers the keypress event |
| keyup() | Attaches/Triggers the keyup event |
| live() | Removed in version 1.9. Adds one or more event handlers to current, or future, selected elements |
| load() | Removed in version 3.0. Attaches an event handler to the load event |
| mousedown() | Attaches/Triggers the mousedown event |
| mouseenter() | Attaches/Triggers the mouseenter event |
| mouseleave() | Attaches/Triggers the mouseleave event |
| mousemove() | Attaches/Triggers the mousemove event |
| mouseout() | Attaches/Triggers the mouseout event |
| mouseover() | Attaches/Triggers the mouseover event |
| mouseup() | Attaches/Triggers the mouseup event |
| off() | Removes event handlers attached with the on() method |
| on() | Attaches event handlers to elements |
| one() | Adds one or more event handlers to selected elements. This handler can only be triggered once per element |
| $.proxy() | Takes an existing function and returns a new one with a particular context |
| ready() | Specifies a function to execute when the DOM is fully loaded |
| resize() | Attaches/Triggers the resize event |
| scroll() | Attaches/Triggers the scroll event |
| select() | Attaches/Triggers the select event |
| submit() | Attaches/Triggers the submit event |
| toggle() | Removed in version 1.9. Attaches two or more functions to toggle between for the click event |
| trigger() | Triggers all events bound to the selected elements |
| triggerHandler() | Triggers all functions bound to a specified event for the selected elements |
| unbind() | Deprecated in version 3.0. Use the off() method instead. Removes an added event handler from selected elements |
| undelegate() | Deprecated in version 3.0. Use the off() method instead. Removes an event handler to selected elements, now or in the future |
| unload() | Removed in version 3.0. Attaches an event handler to the unload event |
The following table lists all the jQuery methods for creating animation effects.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| animate() | Runs a custom animation on the selected elements |
| clearQueue() | Removes all remaining queued functions from the selected elements |
| delay() | Sets a delay for all queued functions on the selected elements |
| dequeue() | Removes the next function from the queue, and then executes the function |
| fadeIn() | Fades in the selected elements |
| fadeOut() | Fades out the selected elements |
| fadeTo() | Fades in/out the selected elements to a given opacity |
| fadeToggle() | Toggles between the fadeIn() and fadeOut() methods |
| finish() | Stops, removes and completes all queued animations for the selected elements |
| hide() | Hides the selected elements |
| queue() | Shows the queued functions on the selected elements |
| show() | Shows the selected elements |
| slideDown() | Slides-down (shows) the selected elements |
| slideToggle() | Toggles between the slideUp() and slideDown() methods |
| slideUp() | Slides-up (hides) the selected elements |
| stop() | Stops the currently running animation for the selected elements |
| toggle() | Toggles between the hide() and show() methods |
The following table lists all the methods used to manipulate the HTML and CSS.
The methods below work for both HTML and XML documents. Exception: the html() method.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| addClass() | Adds one or more class names to selected elements |
| after() | Inserts content after selected elements |
| append() | Inserts content at the end of selected elements |
| appendTo() | Inserts HTML elements at the end of selected elements |
| attr() | Sets or returns attributes/values of selected elements |
| before() | Inserts content before selected elements |
| clone() | Makes a copy of selected elements |
| css() | Sets or returns one or more style properties for selected elements |
| detach() | Removes selected elements (keeps data and events) |
| empty() | Removes all child nodes and content from selected elements |
| hasClass() | Checks if any of the selected elements have a specified class name |
| height() | Sets or returns the height of selected elements |
| html() | Sets or returns the content of selected elements |
| innerHeight() | Returns the height of an element (includes padding, but not border) |
| innerWidth() | Returns the width of an element (includes padding, but not border) |
| insertAfter() | Inserts HTML elements after selected elements |
| insertBefore() | Inserts HTML elements before selected elements |
| offset() | Sets or returns the offset coordinates for selected elements (relative to the document) |
| offsetParent() | Returns the first positioned parent element |
| outerHeight() | Returns the height of an element (includes padding and border) |
| outerWidth() | Returns the width of an element (includes padding and border) |
| position() | Returns the position (relative to the parent element) of an element |
| prepend() | Inserts content at the beginning of selected elements |
| prependTo() | Inserts HTML elements at the beginning of selected elements |
| prop() | Sets or returns properties/values of selected elements |
| remove() | Removes the selected elements (including data and events) |
| removeAttr() | Removes one or more attributes from selected elements |
| removeClass() | Removes one or more classes from selected elements |
| removeProp() | Removes a property set by the prop() method |
| replaceAll() | Replaces selected elements with new HTML elements |
| replaceWith() | Replaces selected elements with new content |
| scrollLeft() | Sets or returns the horizontal scrollbar position of selected elements |
| scrollTop() | Sets or returns the vertical scrollbar position of selected elements |
| text() | Sets or returns the text content of selected elements |
| toggleClass() | Toggles between adding/removing one or more classes from selected elements |
| unwrap() | Removes the parent element of the selected elements |
| val() | Sets or returns the value attribute of the selected elements (for form elements) |
| width() | Sets or returns the width of selected elements |
| wrap() | Wraps HTML element(s) around each selected element |
| wrapAll() | Wraps HTML element(s) around all selected elements |
| wrapInner() | Wraps HTML element(s) around the content of each selected element |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| add() | Adds elements to the set of matched elements |
| addBack() | Adds the previous set of elements to the current set |
| andSelf() | Deprecated in version 1.8. An alias for addBack() |
| children() | Returns all direct children of the selected element |
| closest() | Returns the first ancestor of the selected element |
| contents() | Returns all direct children of the selected element (including text and comment nodes) |
| each() | Executes a function for each matched element |
| end() | Ends the most recent filtering operation in the current chain, and return the set of matched elements to its previous state |
| eq() | Returns an element with a specific index number of the selected elements |
| filter() | Reduce the set of matched elements to those that match the selector or pass the function's test |
| find() | Returns descendant elements of the selected element |
| first() | Returns the first element of the selected elements |
| has() | Returns all elements that have one or more elements inside of them |
| is() | Checks the set of matched elements against a selector/element/jQuery object, and return true if at least one of these elements matches the given arguments |
| last() | Returns the last element of the selected elements |
| map() | Passes each element in the matched set through a function, producing a new jQuery object containing the return values |
| next() | Returns the next sibling element of the selected element |
| nextAll() | Returns all next sibling elements of the selected element |
| nextUntil() | Returns all next sibling elements between two given arguments |
| not() | Returns elements that do not match a certain criteria |
| offsetParent() | Returns the first positioned parent element |
| parent() | Returns the direct parent element of the selected element |
| parents() | Returns all ancestor elements of the selected element |
| parentsUntil() | Returns all ancestor elements between two given arguments |
| prev() | Returns the previous sibling element of the selected element |
| prevAll() | Returns all previous sibling elements of the selected element |
| prevUntil() | Returns all previous sibling elements between two given arguments |
| siblings() | Returns all sibling elements of the selected element |
| slice() | Reduces the set of matched elements to a subset specified by a range of indices |
AJAX is the art of exchanging data with a server, and update parts of a web page - without reloading the whole page.
The following table lists all the jQuery AJAX methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| $.ajax() | Performs an async AJAX request |
| $.ajaxPrefilter() | Handle custom Ajax options or modify existing options before each request is sent and before they are processed by $.ajax() |
| $.ajaxSetup() | Sets the default values for future AJAX requests |
| $.ajaxTransport() | Creates an object that handles the actual transmission of Ajax data |
| $.get() | Loads data from a server using an AJAX HTTP GET request |
| $.getJSON() | Loads JSON-encoded data from a server using a HTTP GET request |
| $.parseJSON() | Deprecated in version 3.0, use JSON.parse() instead. Takes a well-formed JSON string and returns the resulting JavaScript value |
| $.getScript() | Loads (and executes) a JavaScript from a server using an AJAX HTTP GET request |
| $.param() | Creates a serialized representation of an array or object (can be used as URL query string for AJAX requests) |
| $.post() | Loads data from a server using an AJAX HTTP POST request |
| ajaxComplete() | Specifies a function to run when the AJAX request completes |
| ajaxError() | Specifies a function to run when the AJAX request completes with an error |
| ajaxSend() | Specifies a function to run before the AJAX request is sent |
| ajaxStart() | Specifies a function to run when the first AJAX request begins |
| ajaxStop() | Specifies a function to run when all AJAX requests have completed |
| ajaxSuccess() | Specifies a function to run when an AJAX request completes successfully |
| load() | Loads data from a server and puts the returned data into the selected element |
| serialize() | Encodes a set of form elements as a string for submission |
| serializeArray() | Encodes a set of form elements as an array of names and values |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| data() | Attaches data to, or gets data from, selected elements |
| each() | Execute a function for each matched element |
| get() | Get the DOM elements matched by the selector |
| index() | Search for a given element from among the matched elements |
| $.noConflict() | Release jQuery's control of the $ variable |
| $.param() | Create a serialized representation of an array or object (can be used as URL query string for AJAX requests) |
| removeData() | Removes a previously-stored piece of data |
| size() | Removed in version 3.0. Use the length property instead. |
| toArray() | Retrieve all the DOM elements contained in the jQuery set, as an array |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| context | Removed in version 3.0. Contains the original context passed to jQuery() |
| jquery | Contains the jQuery version number |
| jQuery.fx.interval | Change the animation firing rate in milliseconds |
| jQuery.fx.off | Globally disable/enable all animations |
| jQuery.support | A collection of properties representing different browser features or bugs (Intended for jQuery's internal use) |
| length | Contains the number of elements in the jQuery object |
All of the methods in this section manipulate the DOM in some manner. A few of them simply change one of the attributes of an element (also listed in the Attributes category), while others set an element's style properties (also listed in the CSS category). Still others modify entire elements (or groups of elements) themselves—inserting, copying, removing, and so on. All of these methods are referred to as "setters," as they change the values of properties.
A few of these methods—such as .attr(), .html(), and .val()—also act as "getters," retrieving information from DOM elements for later use.
Adds the specified class(es) to each element in the set of matched elements.
Insert content, specified by the parameter, after each element in the set of matched elements.
Insert content, specified by the parameter, to the end of each element in the set of matched elements.
Insert every element in the set of matched elements to the end of the target.
Get the value of an attribute for the first element in the set of matched elements or set one or more attributes for every matched element.
Insert content, specified by the parameter, before each element in the set of matched elements.
Create a deep copy of the set of matched elements.
Get the value of a computed style property for the first element in the set of matched elements or set one or more CSS properties for every matched element.
Remove the set of matched elements from the DOM.
Remove all child nodes of the set of matched elements from the DOM.
Determine whether any of the matched elements are assigned the given class.
Get the current computed height for the first element in the set of matched elements or set the height of every matched element.
Get the HTML contents of the first element in the set of matched elements or set the HTML contents of every matched element.
Get the current computed inner height (including padding but not border) for the first element in the set of matched elements or set the inner height of every matched element.
Get the current computed inner width (including padding but not border) for the first element in the set of matched elements or set the inner width of every matched element.
Insert every element in the set of matched elements after the target.
Insert every element in the set of matched elements before the target.
An object containing all CSS properties that may be used without a unit. The .css() method uses this object to see if it may append px to unitless values.
Modify and filter HTML strings passed through jQuery manipulation methods.
Get the current coordinates of the first element, or set the coordinates of every element, in the set of matched elements, relative to the document.
Get the current computed outer height (including padding, border, and optionally margin) for the first element in the set of matched elements or set the outer height of every matched element.
Get the current computed outer width (including padding, border, and optionally margin) for the first element in the set of matched elements or set the outer width of every matched element.
Get the current coordinates of the first element in the set of matched elements, relative to the offset parent.
Insert content, specified by the parameter, to the beginning of each element in the set of matched elements.
Insert every element in the set of matched elements to the beginning of the target.
Get the value of a property for the first element in the set of matched elements or set one or more properties for every matched element.
Remove the set of matched elements from the DOM.
Remove an attribute from each element in the set of matched elements.
Remove a single class, multiple classes, or all classes from each element in the set of matched elements.
Remove a property for the set of matched elements.
Replace each target element with the set of matched elements.
Replace each element in the set of matched elements with the provided new content and return the set of elements that was removed.
Get the current horizontal position of the scroll bar for the first element in the set of matched elements or set the horizontal position of the scroll bar for every matched element.
Get the current vertical position of the scroll bar for the first element in the set of matched elements or set the vertical position of the scroll bar for every matched element.
Get the combined text contents of each element in the set of matched elements, including their descendants, or set the text contents of the matched elements.
Add or remove one or more classes from each element in the set of matched elements, depending on either the class’s presence or the value of the state argument.
Remove the parents of the set of matched elements from the DOM, leaving the matched elements in their place.
Get the current value of the first element in the set of matched elements or set the value of every matched element.
Get the current computed width for the first element in the set of matched elements or set the width of every matched element.
Wrap an HTML structure around each element in the set of matched elements.
Wrap an HTML structure around all elements in the set of matched elements.
Wrap an HTML structure around the content of each element in the set of matched elements.